Introduction: When Healthcare Gets AI Right, Everyone Can Learn
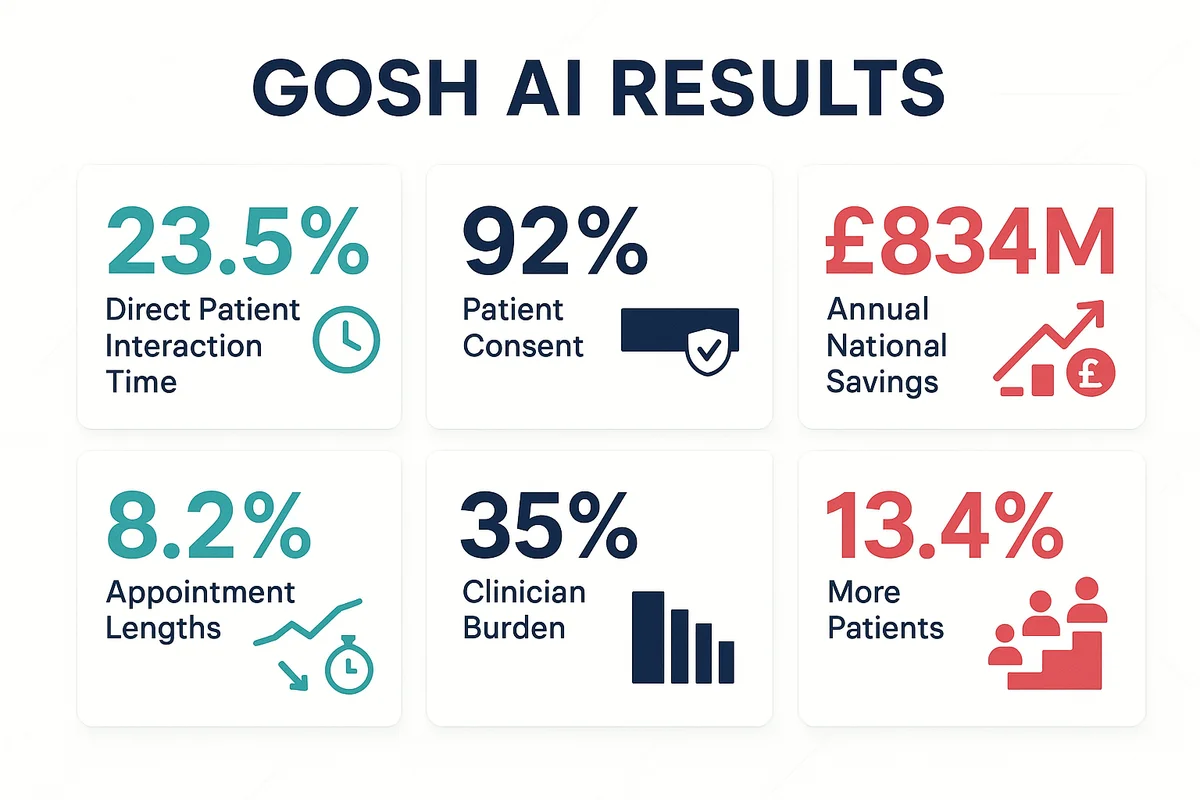
Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) achieved something remarkable in 2024-25: a 23.5% increase in direct patient interaction time, an 8.2% reduction in appointment lengths, and 92% patient consent for AI use. These aren’t marginal gains—they represent transformative efficiency improvements that translate to £834 million in annual national potential when scaled across NHS A&E departments.
What makes GOSH’s AI Scribe implementation particularly instructive isn’t the technology itself—it’s the methodology. Whilst healthcare faces unique regulatory pressures, the core principles driving GOSH’s success apply universally: process-first thinking, rigorous user consent, measurable outcomes, and human-led integration. This case study demonstrates how organisations across finance, retail, professional services, and manufacturing can achieve similar efficiency gains by learning from healthcare’s disciplined approach to AI deployment.
The trial, conducted across nine London NHS sites evaluating over 17,000 patient encounters, provides a robust evidence base that transcends sectoral boundaries. When healthcare organisations—traditionally cautious about technology adoption—achieve these results, the lessons become impossible to ignore.
The GOSH Implementation: Process Transformation, Not Tool Deployment
GOSH’s approach to implementing TORTUS AI-scribe technology reveals a critical distinction: they didn’t deploy AI to automate tasks—they redesigned workflows around AI capabilities whilst maintaining human oversight.
The Process-First Framework
The trial began with systematic workflow analysis across hospitals, GP practices, mental health services, and ambulance teams. Rather than imposing technology on existing processes, GOSH mapped current documentation workflows, identified friction points, and designed AI integration points that enhanced rather than replaced clinical judgement.
This process-first approach manifested in three key areas:
Documentation workflow redesign: Clinicians continued their natural consultation style whilst ambient voice technology captured interactions. The AI generated draft clinical notes for clinician review and approval—not automated completion. This preserved professional accountability whilst eliminating transcription burden.
Patient interaction optimisation: With administrative burden reduced, clinicians redirected time toward patient engagement. The 23.5% increase in direct interaction time wasn’t just about efficiency—it improved diagnostic accuracy and patient satisfaction. In A&E settings, this translated to a 13.4% increase in patients seen per shift at St George’s University Hospital.
Quality assurance integration: Every AI-generated note underwent clinical review before submission. This human-in-the-loop approach ensured accuracy whilst building clinician trust in the system.
The Consent Strategy That Achieved 92% Adoption
GOSH’s 92% patient consent rate wasn’t accidental—it resulted from transparent communication and opt-in design. Patients understood exactly what data would be captured, how AI would process it, and what human oversight remained in place. This consent framework addresses the primary barrier to AI adoption: trust erosion through opaque implementation.
Measurable Outcomes That Justify Investment
Economic modelling by York Health Economics Consortium quantified national implementation potential at £834 million annually: £176 million in documentation time savings and £658 million in unlocked capacity. These figures emerged from rigorous measurement during the trial, providing evidence-based justification for broader deployment.
Qualitative outcomes reinforced quantitative gains: 35% reduction in clinicians feeling overwhelmed by note-taking, improved documentation accuracy, and enhanced patient engagement during consultations.
Cross-Sector Translation: The GOSH Blueprint Beyond Healthcare
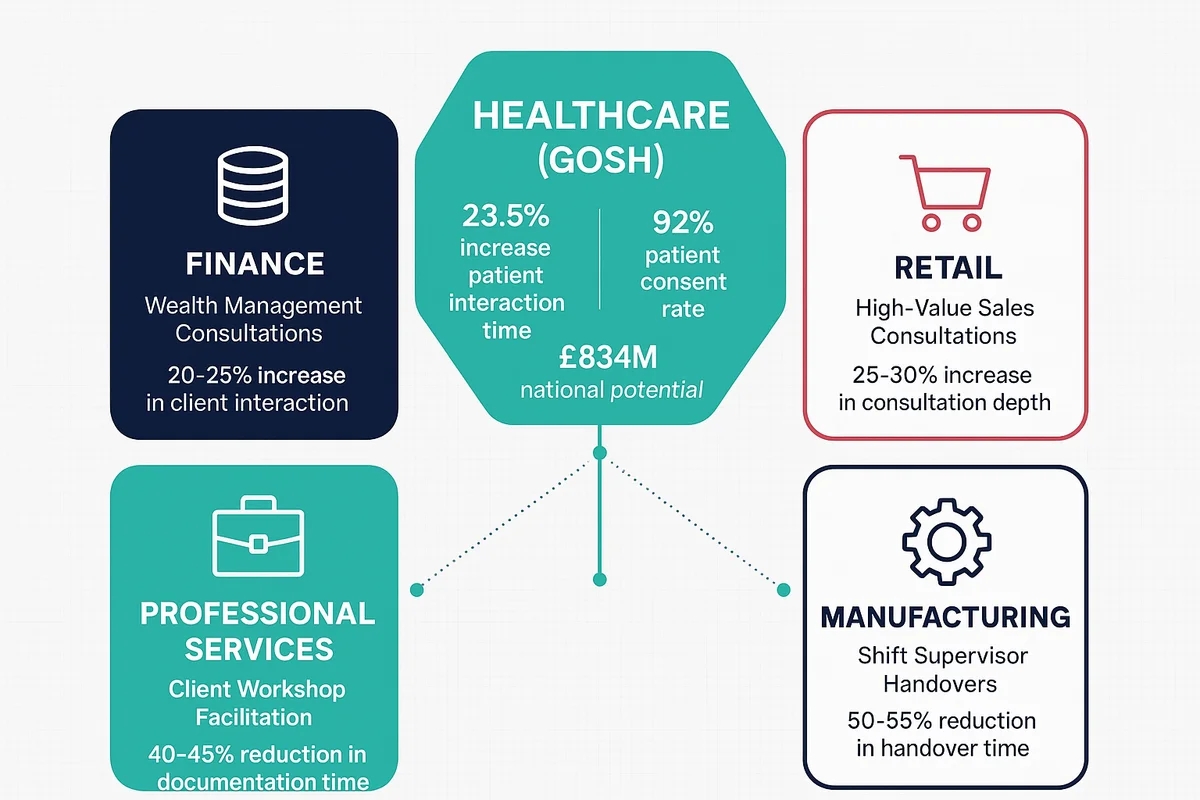
The GOSH implementation provides a replicable framework for organisations seeking efficiency gains through AI. Here’s how the process-first, consent-driven, measurement-focused approach translates across sectors.
Finance: Client Interaction and Compliance Documentation
Financial services face documentation burdens comparable to healthcare—regulatory compliance, client interaction records, and transaction notes consume significant professional time.
Wealth management consultations: Financial advisors conducting client portfolio reviews could deploy ambient AI to capture discussion points, risk disclosures, and investment decisions. This mirrors GOSH’s clinical consultation model—professionals focus entirely on client needs whilst AI handles documentation. Expected outcome: 20-25% increase in meaningful client interaction time, improved compliance documentation accuracy.
Mortgage and loan processing: Customer-facing staff processing applications spend substantial time documenting eligibility discussions, risk assessments, and compliance requirements. AI-assisted note-taking allows advisors to maintain eye contact and build rapport whilst ensuring complete regulatory documentation. Expected outcome: 15-20% reduction in application processing time, improved customer satisfaction scores.
Audit and compliance interviews: Internal auditors conducting control testing or compliance reviews could use AI scribes to capture findings, control assessments, and recommendation discussions. This allows auditors to focus on probing questions and professional scepticism rather than simultaneous documentation. Expected outcome: 10-15% increase in controls tested per audit cycle, enhanced finding quality.
Retail: Customer Service and Operational Efficiency
Retail environments feature high-volume customer interactions and complex operational processes where administrative burden limits service quality.
High-value sales consultations: Luxury retail, automotive showrooms, or technology specialists conducting complex sales interactions could use AI to document customer preferences, product configurations, and follow-up requirements. Sales professionals maintain full attention on customer needs whilst AI captures comprehensive interaction records. Expected outcome: 25-30% increase in consultation depth, improved post-sale follow-up effectiveness.
Store manager operational rounds: Store managers conducting daily operational checks—inventory discrepancies, visual merchandising compliance, staff performance observations—could use voice-based AI documentation. This transforms operational rounds from clipboard exercises to real-time problem-solving. Expected outcome: 30-35% reduction in administrative time, faster issue resolution.
Customer complaint resolution: Customer service representatives handling complex complaints could deploy AI to document issue details, resolution steps, and customer sentiment. Representatives focus entirely on empathetic problem-solving whilst AI ensures complete interaction records for quality assurance. Expected outcome: 20-25% reduction in call handling time, improved first-contact resolution rates.
Professional Services: Client Delivery and Knowledge Capture
Consultancies, law firms, and professional services organisations face billable hour pressures and knowledge management challenges that mirror healthcare’s efficiency concerns.
Client workshop facilitation: Consultants facilitating strategy workshops, requirements gathering, or design thinking sessions could use AI to capture discussion points, decisions, and action items. Facilitators remain fully engaged in guiding productive conversations rather than managing note-taking. Expected outcome: 40-45% reduction in post-workshop documentation time, improved deliverable quality.
Legal client interviews: Solicitors conducting initial client consultations or witness interviews could deploy AI to document case details, legal concerns, and evidence requirements. Lawyers focus entirely on legal analysis and client counsel whilst AI handles comprehensive note-taking. Expected outcome: 20-25% increase in billable client interaction time, enhanced case documentation completeness.
Technical audit fieldwork: IT auditors or management consultants conducting fieldwork interviews could use AI to capture control descriptions, process narratives, and technical specifications. Auditors direct full attention to probing questions and analytical thinking. Expected outcome: 30-35% increase in fieldwork productivity, improved working paper quality.
Manufacturing: Shift Handovers and Continuous Improvement
Manufacturing operations require precise documentation of quality issues, safety observations, and operational changes—activities that often detract from production oversight.
Shift supervisor handovers: Production supervisors conducting end-of-shift handovers could use AI to document equipment status, production variances, quality issues, and safety incidents. Supervisors communicate naturally whilst AI generates structured handover notes for incoming shifts. Expected outcome: 50-55% reduction in handover documentation time, improved cross-shift information continuity.
Quality inspection rounds: Quality engineers conducting production line inspections could use voice-based AI to document observations, non-conformances, and corrective actions. Engineers maintain full focus on visual inspection and technical assessment. Expected outcome: 35-40% increase in inspection coverage, faster quality issue identification.
Continuous improvement workshops: Lean manufacturing or Six Sigma facilitators running kaizen events or problem-solving sessions could deploy AI to capture improvement ideas, root cause analyses, and implementation plans. Facilitators guide productive discussions without documentation distraction. Expected outcome: 30-35% increase in implemented improvements, enhanced knowledge retention.
Human-Context Integration: Why GOSH Succeeded Where Others Struggle
GOSH’s implementation success stems from understanding a fundamental truth: AI amplifies human capability when integrated thoughtfully, but replaces human judgement poorly when deployed carelessly.
The Human-Led AI Principle
GOSH maintained clinical authority throughout implementation. Clinicians reviewed every AI-generated note, made corrections, and exercised professional judgement on content inclusion. The AI served as an intelligent assistant, not an autonomous decision-maker. This human-led approach achieved two critical outcomes: preserved professional accountability and built user trust through transparent limitations.
Organisations pursuing similar implementations must resist the temptation to automate human oversight. The efficiency gains emerge from reducing administrative burden—not from eliminating human judgement. When professionals redirect time from transcription to expertise application, value creation accelerates dramatically.
Process Transformation Over Tool Adoption
GOSH didn’t simply install AI and hope for improvements—they redesigned workflows to leverage AI capabilities whilst addressing its limitations. This process transformation mindset differentiates successful implementations from failed pilots.
Consider the alternative approach: deploying AI without workflow redesign creates friction as users force-fit technology into incompatible processes. GOSH avoided this trap by mapping ideal workflows first, then identifying where AI could eliminate specific friction points.
Organisations should approach AI implementation as process transformation projects, not technology purchases. The question isn’t “How can we automate this task?” but rather “How should this process work ideally, and where can AI reduce burden?”
Measurable Outcomes as Implementation Guides
GOSH’s rigorous measurement served dual purposes: justifying continued investment and identifying improvement opportunities. The 23.5% efficiency gain wasn’t a post-implementation surprise—it emerged from disciplined measurement throughout the trial.
Organisations must establish clear metrics before implementation: baseline measurements, target outcomes, and continuous monitoring mechanisms. Without measurement discipline, AI implementations drift into unsubstantiated optimism or premature abandonment.
Conclusion: Your Process-First AI Implementation Pathway
The GOSH blueprint demonstrates that transformative AI efficiency gains require neither bleeding-edge technology nor massive budgets—they require disciplined implementation methodology. The core principles translate universally:
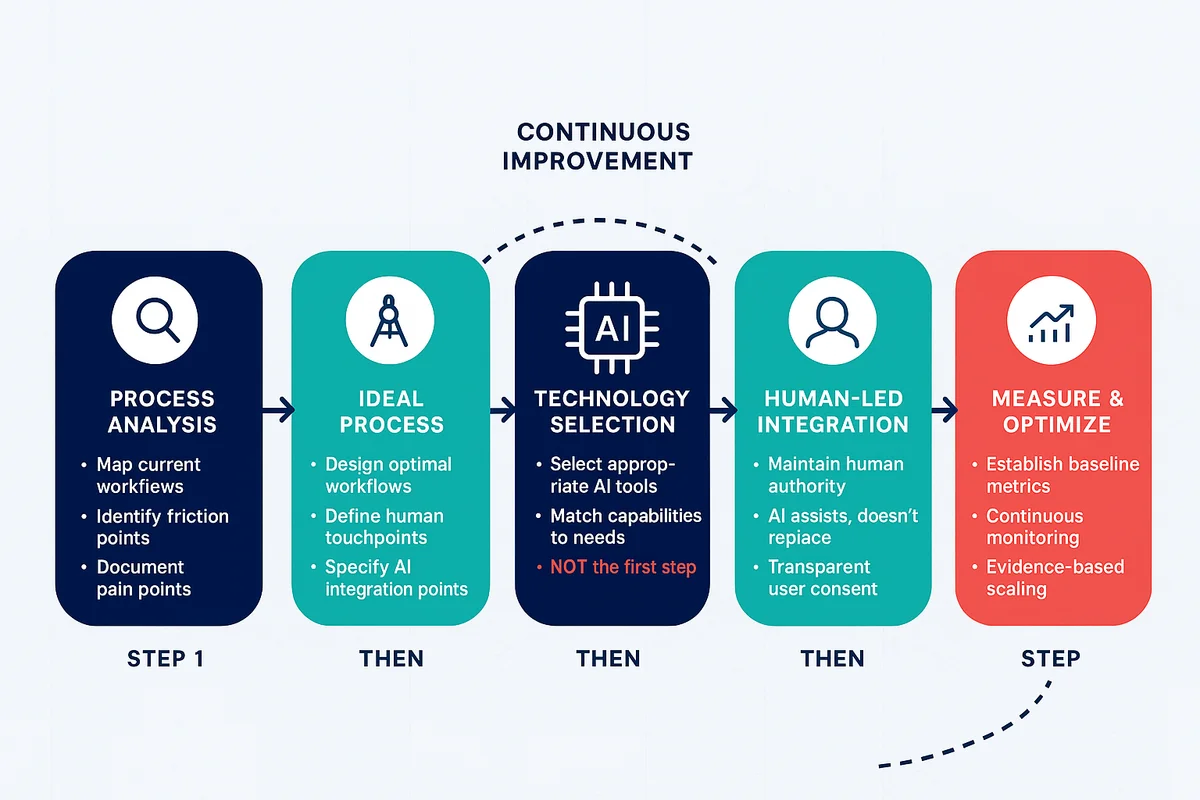
Start with process analysis: Map current workflows, identify administrative friction, and design ideal processes before selecting technology.
Prioritise user consent and transparency: Whether patients, customers, or colleagues, stakeholders must understand how AI processes their interactions and where human oversight remains.
Maintain human authority: AI should reduce burden, not replace judgement. Keep professionals in decision-making roles whilst eliminating transcription and documentation drudgery.
Measure rigorously: Establish baseline metrics, set clear targets, and monitor outcomes continuously. Evidence-based implementation prevents both premature abandonment and uncritical continuation.
Scale based on evidence: GOSH’s trial provided the evidence base for national NHS guidance and broader deployment. Pilot thoroughly, measure carefully, then scale systematically.
The 92% consent rate GOSH achieved reveals another critical insight: when AI implementation genuinely improves outcomes and maintains transparency, user adoption follows naturally. Resistance typically signals poor implementation design, not technology aversion.
If your organisation faces similar efficiency challenges—professionals spending excessive time on documentation, customer interactions shortened by administrative burden, or expertise diluted by transcription duties—the GOSH blueprint provides a proven pathway. The question isn’t whether AI can deliver 20-30% efficiency gains across sectors—GOSH demonstrated it can. The question is whether your organisation will adopt the disciplined, process-first, human-led approach that makes those gains sustainable.
Ready to explore how process-first AI implementation could transform your operations? We offer a free process workflow assessment to identify specific efficiency opportunities in your organisation. Contact us to discuss how healthcare’s implementation lessons translate to your operational context.
